Ten Steps to Kanban Design
Steps 8-10

Design Stockpoint(s)
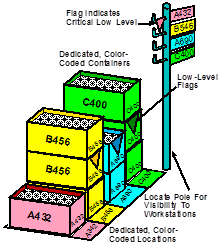
Task eight designs the stockpoint and this design should specify at least the following:
- Location(s)
- Physical Layout Drawing
- Part# Labels
- Maximum Quantities
- Signal Mechanism & Signal Aids
The ideal location for the Stockpoint is near the upstream workcenter. Placing it there helps those operators to monitor the levels and make production decisions that maintain proper levels. However, the location might be at the downstream location or at some intermediate location, provided that the signal mechanism is simple, clear and fast. There might also be a primary Stockpoint at the upstream location with a smaller Stockpoint at the using location, often referred to as Line Stock.
The stockpoint should have a dedicated location for each SKU or item. Each location should be clearly labeled along with some visual guide indicating stock levels. If at all possible, make labels and indicators large enough that the producing workcenter operators can determine their stock status without leaving their workstations.
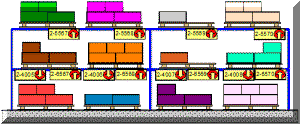
Figure 9 shows examples of stockpoints and illustrated the wide variety of possible designs.
Stockpoint Examples

 Develop Upstream
Scheduling Algorithm
Develop Upstream
Scheduling Algorithm
Kanban signals are sent to the producing workcenter as cards, containers, lights, visual indications or in some other form. In the very simple case where the workcenter makes only one item for a single downstream customer, the scheduling problem is simple: either build or do not build. When that upstream workcenter makes multiple products and/or sends products to multiple customers, some method of scheduling must be in place to decide what to make, when and where to send it.
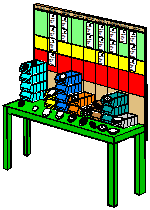
In most instances, the operators can develop these methods and make these decisions. However, it will be helpful to design the initial system and give operators a starting point for future development. When cards are used for the signal, a Kanban Board as in Figure below provides a simple and effective method.

Operate & Fine Tune
The real test of the design is actual operation in production. Here we fine-tune and modify the system as necessary. Such modifications might include changes or improvements to the signal system, containers or any other aspect of the design. However, the common changes are in the maximum Kanban quantity and the number of containers or cards when containers or cards are used.
Monitoring the quantities is a matter of tracking the stock level over a period of days or weeks. The stock level is then adjusted and/or process changes are made that reduce the need for stock.
Summation
In this short paper we have looked at ten steps that will guide engineers through the design of a Kanban system. Much has necessarily been omitted. For example, Kanban should be part of a larger system for production and inventory control that will likely include other methods as well. Kanban is not suitable for every situation. Also omitted is the detail and nuance that is part of every engineering design.
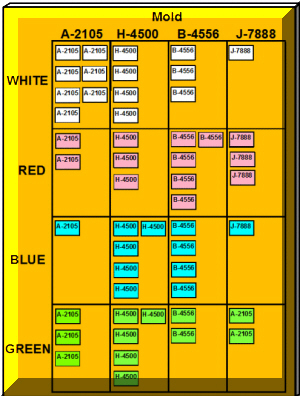
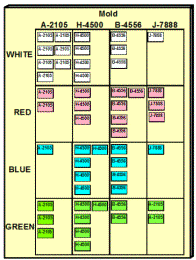
The board in Figure 10 is for an injection molding operation. This workcenter produces 16 items for one downstream workcenter. If there were multiple customers the cards would be assigned to particular customers. Some additional points are:
- 4 Molds
- 4 Colors
- Color Change – 0.75 min
- Mold Change – 25.0 min
- Each Card = 100 pcs
- Usage = 800 pcs/day for each item
- Each item has 8 cards
Since a mold changeover is much longer than a color change, it is best to run all the colors for a given mold once it is in the machine. However, we should not run more than the quantity represented by the available kanban cards. Also, if a particular item is in very short supply, it may be necessary to run that job immediately even if it forces an additional mold change.
 Cards that are not on the board represent parts that have been built and sent to the Stockpoint. Therefore, the more cards showing on the board, the
lower the available stock.
Cards that are not on the board represent parts that have been built and sent to the Stockpoint. Therefore, the more cards showing on the board, the
lower the available stock.
The current status shows that only 100 units of A-2105-White are available. This is less than one hour of average usage. Therefore, the operators need to immediately change to the A-2105 mold and replenish the white parts. Once the white parts are made, they would run the other colors of A-2105 until the board is empty of A-2105 parts. The cards now on the board would be matched to their parts as the parts are made and sent to the Stockpoint along with those parts.
The H-4500 would probably be the next mold change. However, the situation would be re-assessed when the A-2105 parts are complete. If there is a tie, i.e. the same number of cards for two items, operators break the tie based on their general knowledge. In fact, one of the advantages of kanban is that the operators use the scheduling algorithm as a guide but supplement it with current information.
Boards are not the only way to schedule kanban. When empty containers are the signaling device, the scheduling system might amount to arranging the containers as they sit on the floor or shelf. The rule is simple: the highest stack of containers has the highest priority.
 References
References
1. HALL, ROBERT, 1983,”Zero Inventories,” Dow-Jones-Irwin, Homewood, Illinois, USA, 1983
2. LEE, QUARTERMAN, Ten Steps to Effective Kanban, Engineering Lean Six Sigma Conference, Conference Proceedings, Orlando, Florida, USA,2017
3. MONDEN, YASUHIRO, Toyota Production System, Third Edition, Industrial Engineering & Management Press, Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 1998.
4. ASHBY, W.R. 1958, Requisite Variety and its implications for the control of complex systems, Cybernetica (Namur) Vo1 1, No 2, 1958.
■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■