Team Training & Coaching
The Virtuous Circle of Team Learning
 Training
for Lean Manufacturing teams should cover many areas.
Among these are Statistical Process Control, Root Cause Analysis, Team Building, and job skills.
As a result of training and application, teams and individuals are more competent. They work
better together in many ways.
Training
for Lean Manufacturing teams should cover many areas.
Among these are Statistical Process Control, Root Cause Analysis, Team Building, and job skills.
As a result of training and application, teams and individuals are more competent. They work
better together in many ways.

- Destructive, emotional conflict evolves to constructive discussion and rational problem solving.
- Decisions get made quickly and with consensus
- Meetings become timely and produce results.
- People help one another.
- The work gets done.
Types of Training
Team Process Training
Team process refers to the activities and relationships within the team. It involves communication, conflict resolution, time management and other activities. Team process also refers to the gradual establishments of behavioral norms, team objectives and bonding.
Members do not possess instinctive knowledge of team processes and they are unlikely to learn effective team processes from their cultural environment. Training can help and we recommend at least a full day of training on team process.
Effective teamwork requires a set of specific skills and behaviors that are not inherent in our culture. Communication is one example. Many potential team members are quite good at talking. Few have effective listening skills. Conflict will arise whenever two or more people interact. Teams need skills that resolve conflict and not just bury it or tolerate it. Teams need to manage their own time and learn to hold effective meetings. Training can develop these and other skills.
Task Training
When team members lack the skills to accomplish their tasks, the team experiences frustration and conflict. Adequate task training can reduce this source of frustration in the critical early days.
Teams often need considerable cross training. Cross training helps the team function if a member is temporarily absent. It also gives each member a better appreciation for the difficulties other members may face. In many workcells, cross training is essential for workers to balance their workload.
Coaching
Training is not enough, however. Most team members have difficulty when they first attempt to apply the principles they learn in the classroom. Coaching bridges this gap. An effective coach helps the team to see where principles and techniques can apply. Much of the learning of team process can only be gained through experience. An effective coach can guide the team through their early experiences and accelerate this learning.
The Virtuous Circle of Team Learning
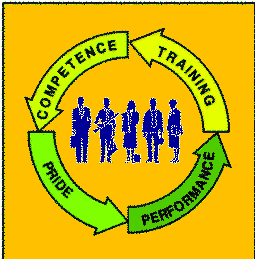 We all know about "Vicious Circles". Teams are in a "Virtuous Circle" in which actions
trigger effects in a cycle that returns to and reinforces the original action. We can trace a
virtuous or vicious circle from anywhere on the loop. Let us arbitrarily start at "Training."
We all know about "Vicious Circles". Teams are in a "Virtuous Circle" in which actions
trigger effects in a cycle that returns to and reinforces the original action. We can trace a
virtuous or vicious circle from anywhere on the loop. Let us arbitrarily start at "Training."
Competence engenders pride for both teams and individuals: Pride in their work, skills, and accomplishments. Pride and competence bring high performance: the "Can Do" and "Will Do".
High performance leads to more training as management sees the benefits. Teams work within their groups to cross-train and assist one another. This renewed training results in higher competence and the Virtuous circle repeats and reinforces.
This virtuous circle is a powerful motivator. It is, for example, the thing that keeps military units together in the worst of battle. Perceptive managers recognize and utilize this effect as part of their Lean Manufacturing Strategy.
What Teams Need
Self Directed Work Teams (SDWT) bring many benefits.
Throwing a group of people together and anointing them as a team will not, however, produce good
results. Effective work teams need.
Team-Oriented Work Structures
Coaching and Training
Task Training
Rewards
Time
Team-Based Culture & Environment
Work Team Structures
Work structure consists of the process and layout. Process includes the operational steps, their sequence, and the required equipment or technology. Layout is the physical arrangement.
Restructuring for Teams
At a manufacturer of custom commercial windows, preparation of an order for production required many activities and more time than the actual production. The activities included sales, engineering, checking, data entry, scheduling, and purchasing. Separate groups at separate physical locations performed these tasks. Every order went through every group. The employees had no common goal and nobody understood the entire process.
A re-organization established three work teams and a new layout co-located team members. Average order processing time went from about 11 weeks to less than one week. In addition errors were reduced.
Team Process Training
Team process refers to the activities and relationships within the team. It involves communication, conflict resolution, time management and other activities. Team process also refers to the gradual establishments of behavioral norms, team objectives and bonding.
Task Training
Teams are especially important for workcells. The work team may not have enough people to assign one skill set to each person. Workloads are often unbalanced. If trouble develops on a particular operation, the team needs to quickly shift members and relieve the problem. For these and other reasons, teams perform better with cross training.
Rewards
Reward systems should be geared to the team rather than individuals. If bonuses and incentives are part of the reward system, they should be given for the team's performance and not individual performance. Intrinsic rewards such as recognition, or feelings of accomplishment have more power than monetary rewards.
Time
Work teams require time to develop and mature. Members master new social and technical skills. The team learns to resolve conflict. Members forge relationships. While some results develop sooner, it usually takes 18-24 months for a team to reach fully potential.
A Team Culture
Managers and specialists who operate outside the work teams must also understand them. Teams can be destroyed by inappropriate personnel policies, pay systems, supervision, or a few destructive comments from managers and staff.
Summary
Self Directed Work Teams are a powerful means to increase productivity, quality, and customer response. They make work more intersting, challenging and satisfying. While these improvements are often-order-of magnitude rather than a few percentage points, they require changes in both management and individual thinking--a paradigm shift. They also require time, effort, and tolerance.
![]()
■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■


